程序设计基础
第五章 函数
第5章 函数
本章要点
- 函数的作用是什么? 如何确定函数功能?
- 怎样定义函数? 如何调用函数? 定义函数与声明函数有何区别?
- 什么是函数的参数? 怎样确定函数的参数?
- 在函数调用时,参数是如何传递数据的?
- 变量与函数有什么关系? 如何使用局部变量和全局变量?
- 什么是静态变量?
5.1 计算圆柱体积
例5-1. 输入圆柱体的高和半径,求圆柱体的体积$volume=\pi\times r^2\times h$,要求定义和调用函数cylinder(r, h)计算圆柱体积
5.1.1 程序解析
#include<stdio.h>
double cylinder(double r, double h); /* 函数声明 */
int main()
{
double height, radius, volumne;
printf("Enter radius and height: ");
scanf("%lf%lf", &radius, &height);
volume=cylinder(radius, height); /* 函数调用,将函数的返回值赋给volume */
printf("Volume=%.3f\n", volume);
return 0;
}
double cylinder(double r, double h) /* 定义函数求圆柱体的体积 */
{
double result;
result=3.1415926*r*r*h; /* 计算体积 */
return result; /* 返回结果 */
}
函数调用是如何运行的?
5.1.2 函数的定义
- 函数是指完成一个特定工作的独立程序模块
- 库函数,由C语言系统提供定义,如scanf, printf等函数
- 自定义函数,需要用户自已定义,如计算圆柱体何种函数cylinder()
- main()也是一个函数,C程序由一个main()或多个函数构成
- 程序中一旦调用了某个函数,该函数就会完成特定的计算,然后
返回到调用它的地方 - 函数经过运算,会得到一个明确的运算结果,并需要回送该结果,如函数cylinder()返回圆柱的体积
函数定义(2)
函数定义形式:
/* 函数首部 函数类型为返回值的类型,与return语句中表达式的类型一致 */
/* 函数类型 double, 函数名 cylinder, 参数列表 double r和double h */
double cylinder(double r, double h) /* 函数首部 */
{ /* 函数体,写在一对大括号内 */
double result; /* 函数内的局部变量 */
result=3.1415926*r*r*h; /* 计算圆柱体积 */
return result; /* 返回运算结果,类型与函数类型一致 */
}
函数参数(形参)
double cylinder(double r, double h)
{
double result;
result=3.1415926*r*r*h;
return result;
}
函数的参数列表必须写成:
参数之间用
5.1.3 函数的调用
- 定义一个函数后,就可以通过程序来调用这个函数
- 调用标准库函数时,在程序的最前面用
#include 命令包含相应的头文件 - 调用自定义函数时,程序中必须有与调用函数相对应的
函数定义
函数调用的形式
- 函数调用的一般形式为:
函数名(实际参数列表) - 对于实现计算功能的函数,函数调用通常会出现在两种情况中
- 赋值语句,如volume=cylinder(radius, height);
- 输出函数的结果,printf("%f", cylinder(radius, height));
函数调用的过程
程序执行
如果遇到函数调用,
函数执行完毕后,
如果调用函数执行过程中遇到return,则直接返回主函数
分析函数调用的过程
见DevC++
#include<stdio.h>
double cylinder(double r, double h); /* 函数声明 */
int main()
{
double height, radius, volumne;
printf("Enter radius and height: ");
scanf("%lf%lf", &radius, &height);
volume=cylinder(radius, height); /* 函数调用 8-->12 */
printf("Volume=%.3f\n", volume);
return 0;
}
double cylinder(double r, double h) /* 参数列表赋值,实参->形参 */
{
double result; /* 执行函数中的语句 */
result=3.1415926*r*r*h;
return result; /* 返回结果到调用的地方,第8行 */
}
参数传递
- 函数
定义 时的参数被称为形式参数 ,简称(形参 )
double cylinder(double r, double h) - 函数
调用 时的参数被称为实际参数 ,简称(实参 )
volume=cylinder(radius, height); - 参数传递,从
实参 -->形参 ,是单向传递 - 在参数传递过程中,实参将值
复制 给形参 - 形参和实参
一一对应 :数量一致,类型一致,顺序一致 形参 : 是变量,用于接受实参传递过来的值实参 : 可以是常量、变量或表达式
函数结果返回
调用函数完成计算后,将运算结果返回给
return 表达式;
return可用于返回函数运算的结果,也可用于终止调用函数的运行。函数只能返回一个值,如需要返回多个值,需采用其它方法实现
函数原型声明
函数声明,只写函数的首部,以分号结束,不包含函数体,即函数的实现部分
double volume(double r, double h);
void pyramid(int n);
- 函数必须
先定义后调用 ,将主调函数放在被调函数的后面,就像变量先定义后使用一样 - 如果自定义函数在主调函数的后面,就需要在函数调用前,加上函数原型声明
- 函数声明,用于说明函数的类型和参数列表,以保证程序编译时能判断对该函数的调用是否正确
5.1.4 函数程序设计
例5-2. 计算五边形的面积
将一个五边形分割成3个三角形,输入这些三角形的7条边长,计算该五边形的面积。要求定义和调用函数area(x,y,z)计算边长为x,y,z的三角形面积
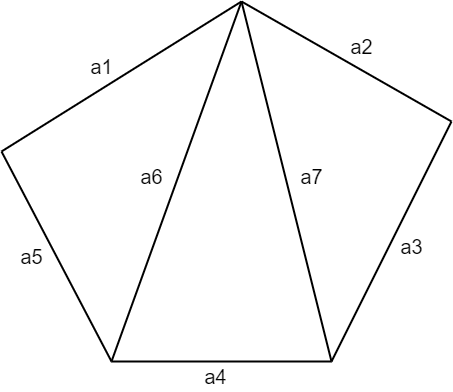
计算五边形面积源程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
double area(double x, double y, double z);
int main()
{
double a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, s;
printf("Please input 7 side lengths in the order a1 to a7:");
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &a1, &a2, &a3, &a4, &a5, &a6, &a7);
s=area(a1, a5, a6)+area(a4, a6, a7)+area(a2, a3, a7); /* 调用三次area函数计算面积 */
printf("The area of the pentagon is %.2f\n", s);
return 0;
}
/* 使用海伦-秦九韶公式计算三角形面积的函数 */
double area(double x, double y, double z)
{
double p=(x+y+z)/2;
return sqrt(p*(p-x)*(p-y)*(p-z));
}
自定义函数程序的优点
- 程序结构清晰,逻辑关系明确,程序可读性强
- 解决相同或相似问题时不用重复编写代码、可通过调用函数解决,减少代码量
- 利用函数实现模块化编程,各模块功能相对独立,利用“各个击破”降低调试难度
练习
练习. 判断奇偶数
定义一个判断奇偶数的函数even(n),当n为偶数时返回1,否则返回0。利用该函数计算1-500之间所有偶数的和
#include<stdio.h>
/* 判断奇偶性的函数 */
int even(int n)
{
if(n%2==0)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* 求1-500之间所有偶数的和 */
int main()
{
int i, sum=0;
for(i=1; i<=500; i++)
{
if(even(i)==1)
sum=sum+i;
}
printf("%d", sum);
return 0;
}
判断完全平方数
例5-3. 判断完全平方数
定义一个判断完全平方数的函数isSquare(n),当n为完全平方数时返回1,否则返回0,不允许使用数学库函数
如果n是完全平方数,则可以找到正整数m使$n=m^2$成立。在
判断完全平方数程序实现
#include<stdio.h>
int isSquare(int n)
{
int i;
for(i=1; n>0; i=i+2)
{
n=n-i;
}
if(n==0)
return 1; /* 是完全平方数返回1 */
else
return 0; /* 不是完全平方数返回0 */
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter n:");
scanf("%d", &n);
if(isSquare(n)==1)
printf("%d is complete square number.\n", n);
else
printf("%d is not a complete square number.\n", n);
}
求最大公约数
例5-4. 求最大公约数
定义函数gcd(int m, int n),计算m和n的最大公约数
辗转相除法(欧几里得算法)
1. temp=m%n
2. 若temp为0,返回n的值,否则转3.
3. m=n, n=temp, 转1继续
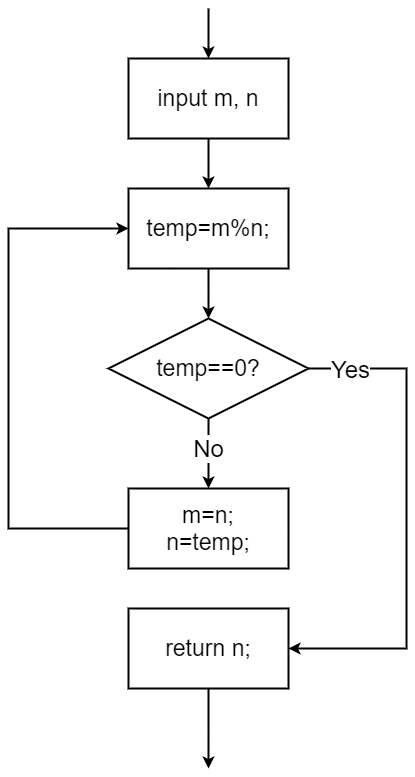
求最大公约数源程序
#include<stdio.h>
int gcd(int m, int n)
{
int r, temp;
if(m<n) /* 保证m比n大 */
{
temp=m;
m=n;
n=temp;
}
r=m%n;
while(r!=0){
m=n;
n=r;
r=m%n;
}
return n;
}
int main()
{
int m, n;
int g;
printf("Enter two numbers m, n(m>n):");
scanf("%d%d", &m, &n);
g=gcd(m, n);
printf("GCD of %d and %d is %d", m, n, g);
return 0;
}
使用函数判断素数
例5-5. 使用函数判断素数
求100以内的全部素数,每行输出10个。素数是只能被1和自身整除的正整数,1不是素数,2是素数。
要求定义和调用函数prime(m)判断m是否为素数,当m为素数时返回1,否则返回0
使用函数判断素数源程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int prime(int m)
{
int i, n, limit;
if(m<=1)
return 0;
else if(m==2)
return 1;
else{
limit=sqrt(m)+1;
for(i=2; i<=limit; i++){
if(m%i==0)
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int count, m;
count=0;
for(m=2; m<=100; m++){
if(prime(m)!=0){
printf("%6d", m);
count++;
if(count%10==0)
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
求$\pi$的近似值
示例. 使用函数求$\pi$的近似值
输入精度e,使用格雷戈里公式求$\pi$的近似值,精确到最后一项的绝对值小于e
$$
\frac{\pi}{4}=\frac{!}-\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{5}-\frac{1}{7}+\cdots
$$
求$\pi$的近似值源程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
double funpi(double e)
{
int denominator, flag;
double item, sum;
flag=1;
denominator=1;
item=1.0;
sum=0;
while(fabs(item)>=e){
sum=sum+item;
flag=-flag;
denominator=denominator+2;
item=flag*1.0/denominator;
}
sum=sum+item;
return sum*4;
}
int main()
{
double e, pi;
printf("Enter e:");
scanf("%lf", &e);
pi=funpi(e);
printf("pi=%f\n", pi);
return 0;
}
5.2 数字金字塔
例5-6. 数字金字塔
输入一个正整数,输出n行数字金字塔。如当n=5时,输出的金字塔如下图所示

- 一行中的空格处理
- 一行中的数字显示
- 每一行的数字、空格处理
5.2.1 程序解析
#include<stdio.h>
void pyramid(int n) /* 函数定义 */
{
int i, j;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++){ /* 需要输出的行数 */
for(j=1; j<=n-i; j++){ /* 输出每行左边的空格 */
printf(" ");
}
for(j=1; j<=i; j++){ /* 输出每行的数字 */
printf("%d ", i); /* 注意每个数字后有空格 */
}
putchar('\n'); /* 换行 */
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter n:");
scanf("%d", &n);
pyramid(n);
return 0;
}
5.2.2 不返回运算结果的函数
{
函数实现体
return;
}
函数定义中,
返回类型为void的函数一般用于输出
不返回运算结果的函数定义
- 由于函数没有返回结果,函数调用不可能出现在表达式中,通常以独立的调用语句方式出现,如pyramid(5)
- 不返回结果的函数,在定义、调用、参数传递、函数声明上,思路与其它函数定义完全相同,只是函数类型为void
- 适用于将一些确定的、相对独立的程序功能包装成函数
- 主函数通过调用不同的函数,体现算法步骤
- 各步骤的实现由相应函数完成
- 简化主函数结构,以体现结构化程序设计思想
结构化程序设计思想
- 结构化程序设计(Structured Programming)是一种程序设计技术,C语言是结构化程序设计语言
- 结构化程序设计强调程序设计的风格和程序结构的规范化,提供清晰的结构
- 其基本思路是将一个复杂问题的求解过程划分为若干阶段,每个阶段要处理的问题都容易被理解和处理
- 按照
自顶向下的方法 对问题进行分析、模块化设计和结构化编码等3个步骤
自顶向下的分析方法
- 将大的复杂的
问题分解 为小问题后再解决 - 面对一个复杂的问题,首先进行上层(整体)的分析,按组织或功能将问题分解成
子问题 - 如果子问题仍然十分复杂,再做进一步的分解,直到处理对象
相对简单 ,容易处理为止 - 当所有的子问题都得到了解决,整个问题也就解决了
- 每一次分解都是对上一层问题进行细化和逐步求精,最终形成一种类似
树形的层次结构 ,来描述分析的结果
学生成绩统计程序的层次结构图
学生成绩统计程序经分解后得到树状结构,每个模块均设计为独立的函数,整个程序通过调用函数实现
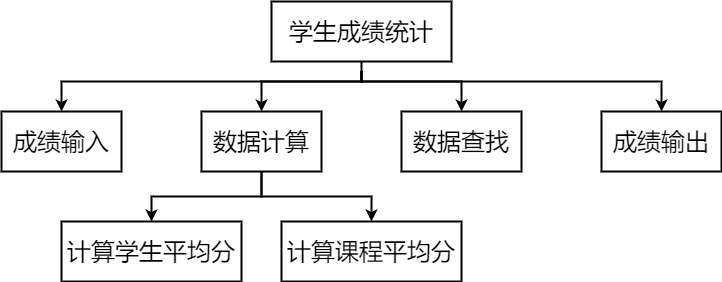
模块化设计
- 模块化设计是将模块组织成良好的层次系统
- 顶层模块调用其下层模块实现程序的完整功能
- 每个下层模块再调用更下层的模块,从而完成程序的每一个子功能
- 最下层的模块完成最具体的功能
- 遵循模块独立性的原则,即模块之间的联系应尽量简单,尽量保持模块之间的独立性
- 模块用函数实现
- 一个模块只完成一个指定的功能
- 模块之间只能通过带参数的函数进行调用
结构化编码的主要原则
- 经过模块化设计后,每一个模块都可以独立编码,编程时应选用顺序、选择和循环三种控制结构
- 对变量、函数、常量等命名时,要见名知意,有助于对变量含义或函数功能的理解
- 在程序中增加必要的注释,增加程序的可读性
- 要有良好的程序视觉组织,利用缩进格式控制页面排版
- 程序要清晰易懂,语句构造要简单直接
- 程序有良好的交互性,输入有提示,输出有说明
5.3 复数运算
例5-7. 计算两个复数的和与积
分别输入两个复数的实部与虚部,用函数实现计算两个复数的和与积
若两个复数分别为: c1=x1+y1
则有
c1+c2=(x1+x2)+(y1+y2)
c1*c2=(x1*x2-y1*y2)+(x1*y2+x2*y1)
5.3.1 程序解析
#include<stdio.h>
double result_real, result_imag; /* 全局变量,用于存放函数结果 */
void complext_add(double real1, double imag1, double real2, double imag2)
{
result_real=real1+real2;
result_imag=imag1+imag2;
}
void complex_prod(double real1, double imag1, double real2, double imag2)
{
result_real=real2*imag1-real1*imag2;
result_imag=real1*imag2+real2*imag1;
}
int main()
{
double real1, real2, imag1, imag2; /* 两个复数的实部和虚部 */
printf("Enter 1st complex number(real and imaginary):");
scanf("%lf%lf", &real1, &imag1);
printf("Enter 2nd complex number(real and imaginary):");
scanf("%lf%lf", &real2, &imag2); /* 分别输入两个复数的实部和虚部 */
complex_add(real1, imag1, real2, imag2); /* 计算两个复数的和 */
printf("addition of complex is %f+%fi\n", result_real, result_imag);
complex_prod(real1, imag1, real2, imag2); /* 计算两个复数的积 */
printf("product of complex is %f+%fi\n", result_real, result_imag);
return 0;
}
5.3.2 全局变量和局部变量
- 局部变量
- 在函数内定义的变量(包括形式参数),作用范围在
本函数内部 - 定义在复合语句内的变量,作用范围在
复合语句内部 - 全局变量
- 在函数以外定义的变量,不从属于任何一个函数,其作用范围是
从定义处到源文件结束(包括各函数)
在复合语句中定义局部变量
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a;
a=1;
{ /* 复合语句开始 */
int b=2;
b=a+b;
a=a+b;
} /* 复合语句结束 */
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
上述代码的输出是什么?如果将11行改为
全局变量定义
#include<stdio.h>
int x; /* 定义全局变量x */
int f()
{
int x=4; /* x是局部变量 */
return x;
}
int main()
{
int a=1;
x=a; /* 对全局变量x赋值 */
a=f(); /* a的值为4 */
{
int b=2;
b=a+b; /* b的值为6 */
x=x+b; /* 全局变量运算, x的值为7 */
}
printf("%d %d", a, x);
return 0;
}
若局部变量与全局变量同名,局部变量优先
变量作用范围示例
int x=1;
void main()
{
int a=2;
//......
{
int b=3; /* x=? a=? b=? */
//......
}
f();
//...... /* b=? */
}
int t=4;
void f()
{
int x=5, b=6; /* x=? a=? b=? t=? */
//......
}
int a=7; /* a=? b=? t=? x=? */
用函数实现财务现金记账
例5-8. 用函数实现财务现金记账
先输入操作类型: 1. 收入,2. 支出,0. 结束。再输入操作金额,计算现金剩余额,经多次操作直到输入操作类型为0时结束。要求定义并调用函数,其中现金收与现金支出分别用不同函数实现
分析:设变量cash保存现金余额值,由于它被主函数、现金收入与现金支出函数共用,任意使用场合其意义与数值都是明确且唯一的,因此将其设为全局变量
现金记账源程序
#include<stdio.h>
double cash; /* 定义全局变量,保存现金余额 */
void income(double number) /* 定义现金收入函数 */
{
cash=cash+number; /* 改变全局变量cash的值 */
}
void expend(double number) /* 定义现金支出函数 */
{
cash=cash-number; /* 改变全局变量cash的值 */
}
int main()
{
int choice;
double value;
cash=0; /* 初始金额为0 */
printf("Enter operation choice(0-end, 1-income, 2-expend):");
scanf("%d", &choice);
while(choice!=0){ /* 若输入类型为0,结束循环 */
if(choice==1 || choice==2){
printf(“Enter cash value:"); /* 输入操作现金额 */
scanf("%f", &value);
if(choice==1)
income(value); /* 函数调用,计算现金收入 */
else
expend(value); /* 函数调用,计算现金支出 */
printf("Current cash: %.2f\n", cash);
}
printf("Enter operation choice(0-end, 1-income, 2-expend):");
scanf("%d", &choice);
}
return 0;
}
关于全局变量和局部变量的思考
- 全局变量比局部变量自由度大,使用更方便?
- 对于规模较大的程序,过多使用全局变量会带来副作用,导致各函数间出现相互干扰。如果整个程序是由多个合作开发,各人都按自己的想法使用全局变量,相互的干扰可能会更严重
- 在变量使用中,应尽量使用局部变量,从某个角度看使用似乎受到了限制,但从另一个角度看,它避免了不同函数间的相互干扰,提高了程序质量
5.3.3 变量生命周期和静态局部变量
- 变量生命周期
- 变量从定义开始分配存储单元,到运行结束存储单元被回收的整个过程
-
自动变量(
auto )
char c1; <-->
函数调用时,定义变量,分配存储单元;当函数调用结束时,收回存储单元
C程序存储分布示意图
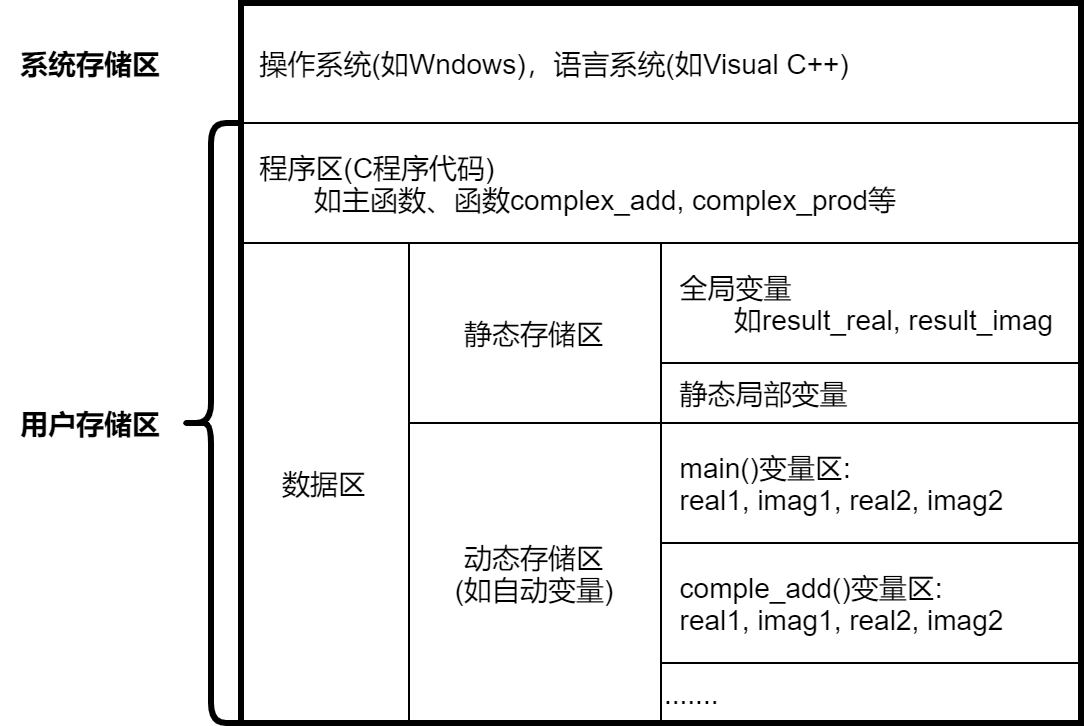
静态局部变量
静态局部变量的作用范围是局部,但其生命周期是存在于全局
计算阶乘
例5-9. 计算阶乘
输入正整数n,输出1!~n!的值。要求定义并调用含静态变量的函数fact_s(n)计算n!
#include<stdio.h>
double fact_s(int n)
{
static double f=1;
f=f*n;
return f;
}
int main()
{
int i, n;
printf("Enter n:");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
printf("%3d!=%.0f\n", i, fact_s(i));
return 0;
}
静态局部变量
- 自动变量如果没有赋初值,其存储单元中将是随机值
- 静态变量,如果定义时没有赋初值,系统将自动赋值为0
- 赋初值只在函数第一次调用时起作用,以后调用都按前一次调用后保留的值使用
- 静态局部变量受变量的作用范围限制,不能作用于其它函数,包括主函数
静态变量与全局变量
- 静态变量与全局变量均位于静态存储区,其共同点是生命周期贯穿整个程序执行过程
- 区别在于,作用范围不同,全局变量可作用于所有函数,静态变量只能用于所定义函数,而不能使用于其它函数